The 1st partition of Poland
The First Partition of Poland or First Partition of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth took place in 1772 as the first of three partitions that ended the existence of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth by 1795. Growth in the Russian Empire's power, threatening the Kingdom of Prussia and the Habsburg Austrian Empire, was the primary motive behind this first partition. Frederick the Great engineered the partition to prevent Austria, jealous of Russian successes against the Ottoman Empire, from going to war.
The weakened Commonwealth's land, including that was already controlled by Russia, was apportioned among its more powerful neighbors—Austria, Russia and Prussia—so as to restore the regional balance of power in Central Europe among those three countries. With Poland unable to effectively defend itself, and with foreign troops already inside the country, the Polish parliament (Sejm) ratified the partition in 1773 during the Partition Sejm convened by the three powers.
On August 5, the three parties signed the treaty on their respective territorial gains on the commonwealth's expense.
In the late 17th and early 18th centuries, the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth had been reduced from the status of a major European power to that of a Russian protectorate (or vassal or satellite state), with the Russian tsar effectively choosing Polish-Lithuanian monarchs during the free elections and deciding the outcome of much of Poland's internal politics, for example during the Repnin Sejm, named after the Russian ambassador who unofficially presided over the proceedings.
The First Partition occurred after the balance of power in Europe shifted, with Russian victories against the Ottomans in the Russo-Turkish War (1768–1774) strengthening Russia and endangering Habsburg interests in that region (particularly in Moldavia and Wallachia). At that point Habsburg Austria started to consider waging a war against Russia.
France, friendly towards both Russia and Austria, suggested a series of territorial adjustments, in which Austria would be compensated by parts of Prussian Silesia, and Prussia in turn would receive Polish Ermland (Warmia) and parts of the Polish fief, Duchy of Courland and Semigallia—already under Baltic German hegemony. King Frederick II of Prussia had no intention of giving up Silesia gained recently in the Silesian Wars; he was, however, also interested in finding a peaceful solution—his alliance with Russia would draw him into a potential war with Austria, and the Seven Years' War had left Prussia's treasury and army weakened. He was also interested in protecting the weakening Ottoman Empire, which could be advantageously utilized in the event of a Prussian war either with Russia or Austria. Frederick's brother, Prince Henry, spent the winter of 1770–71 as a representative of the Prussian court at Saint Petersburg. As Austria had annexed 13 towns in the Hungarian Szepes region in 1769 (violating the Treaty of Lubowla), Catherine II of Russia and her advisor General Ivan Chernyshyov suggested to Henry that Prussia claim some Polish land, such as Ermland. After Henry informed him of the proposal, Frederick suggested a partition of the Polish borderlands by Austria, Prussia, and Russia, with the largest share going to the party most weakened by the recent changes in balance of power, Austria. Thus Frederick attempted to encourage Russia to direct its expansion towards weak and non-functional Poland instead of the Ottomans.[3] Austrian statesman, Wenzel Anton Graf Kaunitz, counter-proposed that Prussia take lands from Poland in return for relinquishing Silesia to Austria, but this plan was rejected by Frederick.
Although for a few decades (since the times of the Silent Sejm) Russia had seen weak Poland as its own protectorate,[1] Poland had also been devastated by a civil war in which the forces of the Bar Confederation attempted to disrupt Russian control over Poland.[3] The recent Koliyivschyna peasant and Cossack uprising in Ukraine also weakened the Polish position. Further, the Russian-supported Polish king, Stanisław August Poniatowski, was seen as both weak and too independent-minded; eventually the Russian court decided that the usefulness of Poland as a protectorate had diminished.[5] The three powers officially justified their actions as a compensation for dealing with troublesome neighbor and restoring order to Polish anarchy (the Bar Confederation provided a convenient excuse); in fact all three were interested in territorial gains.[6]
After Russia occupied the Danubian Principalities, Henry convinced Frederick and Archduchess Maria Theresa of Austria that the balance of power would be maintained by a tripartite division of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth instead of Russia taking land from the Ottomans. Under pressure from Prussia, which for a long time wanted to annex the northern Polish province of Royal Prussia, the three powers agreed on the First Partition of Poland. This was in light of the possible Austrian-Ottoman alliance[7] with only token objections from Austria,[5] which would have instead preferred to receive more Ottoman territories in the Balkans, a region which for a long time had been coveted by the Habsburgs. The Russians also withdrew from Moldavia away from the Austrian border. An attempt of Bar Confederates to kidnap king Poniatowski on 3 November 1771 gave the three courts another pretext to showcase the "Polish anarchy" and the need for its neighbors to step in and "save" the country and its citizens.
Already by 1769—71, both Austria and Prussia had taken over some border territories of the Commonwealth, with Austria taking Szepes County in 1769–1770 and Prussia incorporating Lauenburg and Bütow.
On February 19, 1772, the agreement of partition was signed in Vienna.
A previous agreement between Prussia and Russia had been made in Saint Petersburg on February 6, 1772.
Early in August, Russian, Prussian and Austrian troops simultaneously entered the Commonwealth and occupied the provinces agreed upon among themselves. On August 5, the three parties signed the treaty on their respective territorial gains on the commonwealth's expense.
The regiments of the Bar Confederation, whose executive board had been forced to leave Austria (which previously supported them) after that country joined the Prusso-Russian alliance, did not lay down their arms. Many fortresses in their command held out as long as possible; Wawel Castle in Kraków fell only at the end of April;Tyniec fortress held until the end of July 1772; Częstochowa, commanded by Kazimierz Pułaski, held until late August.
In the end, the Bar Confederation was defeated, with its members either fleeing abroad or being deported to Siberia by the Russians.
The partition treaty was ratified by its signatories on September 22, 1772.
It was a major success for Frederick II of Prussia:
Prussia's share might have been the smallest, but it was also significantly developed and strategically important.
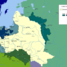
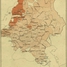
Prussia took most of Polish Royal Prussia, including Ermland, allowing Frederick to link East Prussia and Brandenburg. Prussia also annexed northern areas of Greater Poland along the Noteć River (the Netze District), and northern Kuyavia, but not the cities of Danzig (Gdańsk) and Thorn (Toruń).
The territories annexed by Prussia became a new province in 1773 called West Prussia. Overall, Prussia gained 36,000 km2 and about 600,000 people. According to Jerzy Surdykowski Frederick the Great soon introduced German colonists on territories he conquered and engaged in Germanization of Polish territories
Frederick II settled 26,000 Germans in Polish Pomerania which influenced the ethnic situation in the region that at the time had around 300,000 inhabitants, and enforced Germanization
According to Christopher Clark in certain areas annexed by Prussia like Notec and Royal Prussia 54 percent of the population 75 percent of the urban populace were German-speaking Protestants.
In the next century this was used by nationalistic German historians to justify the partition, but it was irrelevant to contemporary calculations; Frederick, dismissive of German culture, was instead pursuing an imperialist policy, acting on the security interests of his state. The new-gained territories connected Prussia with Germany proper, and were of major economic importance.
By seizing northwestern Poland, Prussia instantly cut off Poland from the sea, and gained control over 80% of the Commonwealth's total foreign trade. Through levying enormous custom duties, Prussia accelerated the inevitable collapse of the Polish-Lithuanian state.
Despite token criticism of the partition from the Austrian archduchess, Empress Maria Theresa, Austrian statesman Wenzel Anton Graf Kaunitz considered the Austrian share an ample compensation; despite Austria being the least interested in the partition, it received the largest share of formerly Polish population, and second largest land share (83,000 km and 2,650,000 people). To Austria fell Zator and Auschwitz (Oświęcim), part of Little Poland embracing parts of the counties of Kraków and Sandomierz (with the rich salt mines of Bochnia and Wieliczka), and the whole of Galicia, less the city of Kraków.
Russia received the largest, but least-important area economically, in the northeast. By this "diplomatic document" Russia came into possession of the commonwealth territories east of the line formed roughly by the Dvina, Drut, and Dnieper Rivers—that section of Livonia which had still remained in commonwealth control, and of Belarus embracing the counties of Vitebsk, Polotsk and Mstislavl.
Russia gained 92,000 square kilometers (36,000 sq mi) and 1,300,000 people, and reorganized its newly acquired lands into Pskov Governorate (which also included two provinces of Novgorod Governorate) and Mogilev Governorate.
Zakhar Chernyshyov was appointed the Governor General of the new territories on May 28, 1772.
By the first partition the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth lost about 211,000 square kilometers (81,000 sq mi) (30% of its territory, amounting at that time to about 733,000 square kilometers (283,000 sq mi)), with a population of over four to five million people (about a third of its population of fourteen million before the partitions).
Related events
Map
Sources: wikipedia.org, news.lv